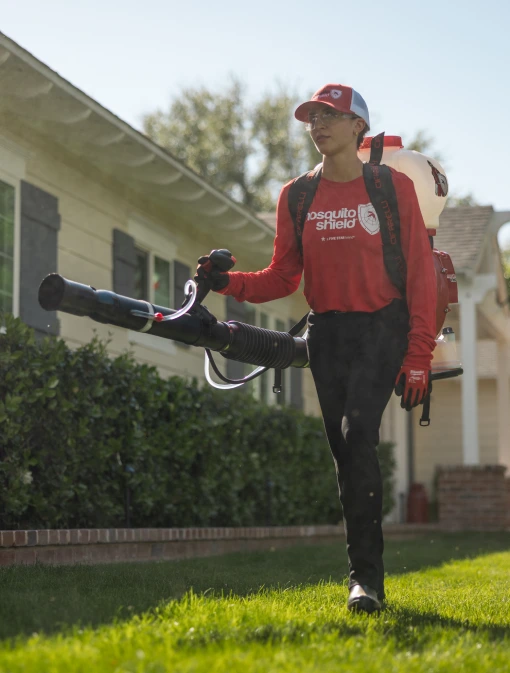
Experience relaxation and peace in your Levittown backyard with our proven mosquito control solution. Trusted by families in Levittown, our innovative approach not only repels mosquitoes but also establishes a durable barrier customized to your outdoor environment. Mosquito Shield of Southeastern PA is dedicated to creating mosquito-free zones, so you can enjoy your outdoor spaces without interruption.
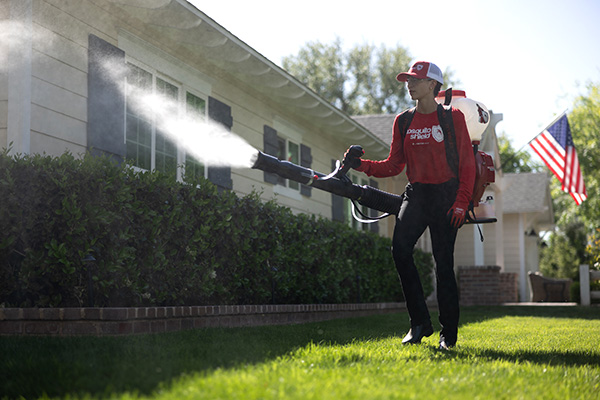

Effective mosquito control in Levittown, PA, that drives mosquitoes away and keeps them out of your yard.
Enjoy mosquito-free outdoor time in Levittown with treatments designed to provide lasting results.

Highly rated mosquito control services in Levittown, trusted by residents to enhance outdoor living.
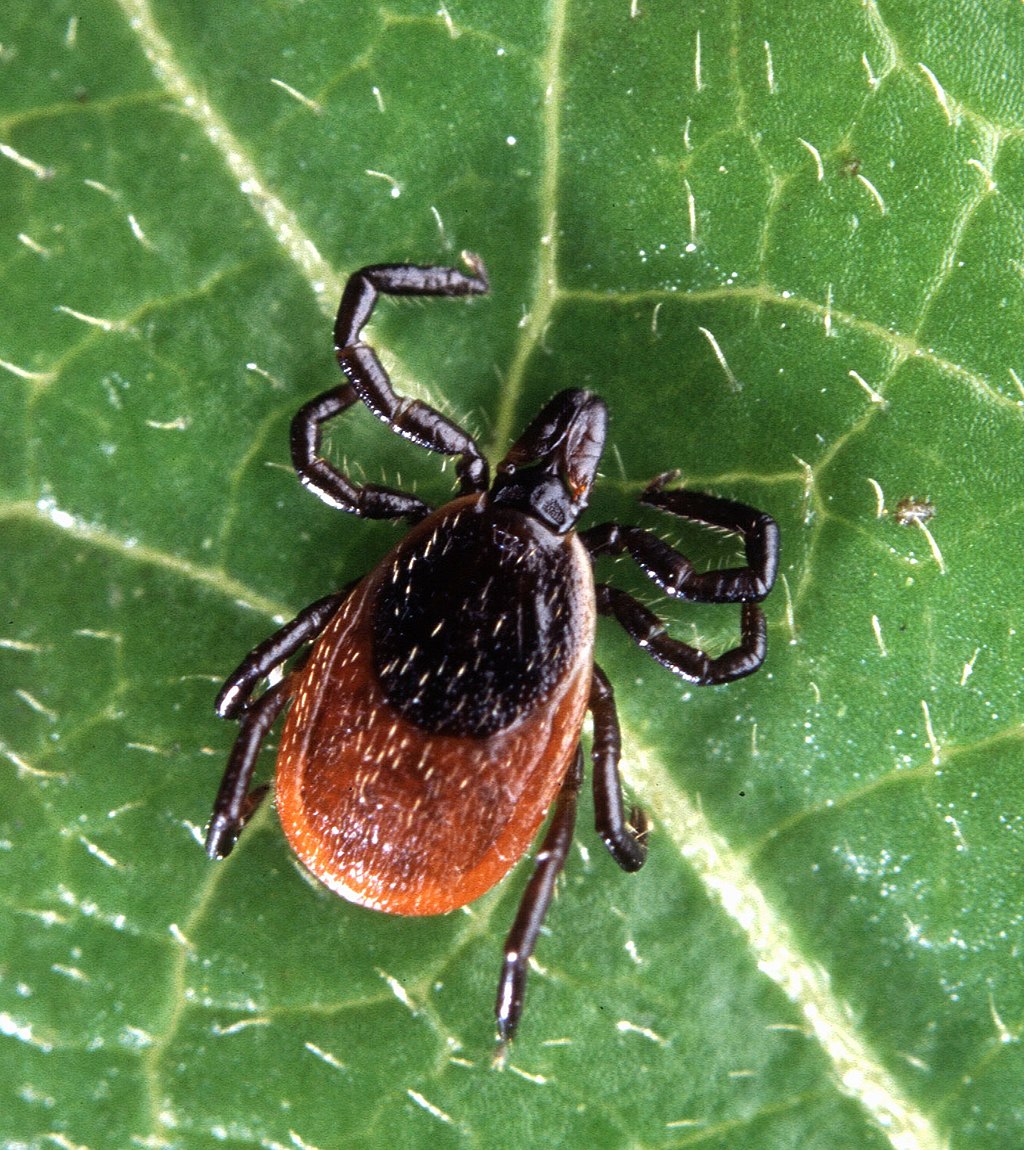


Deer ticks are small but dangerous, and they're a year-round concern in Southeastern PA. Adult females have a reddish-brown body with a dark dorsal plate, while nymphs are nearly invisible.
These ticks are often found in wooded areas, leaf piles, overgrown yards, and along the edge of hiking trails.
They are the main culprits behind Lyme disease, and can also carry anaplasmosis, babesiosis, ehrlichiosis, and Powassan virus. Tick checks after time outdoors are critical in this region.

Wood ticks are larger and easier to spot, with reddish-brown coloring and silvery white markings. They're prevalent in grassy fields, hiking paths, and suburban parks.
These ticks often latch onto pets and people after outdoor activities.
While they don’t spread Lyme disease, they can carry Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia, and their bites can lead to irritation or secondary infection if not removed properly.
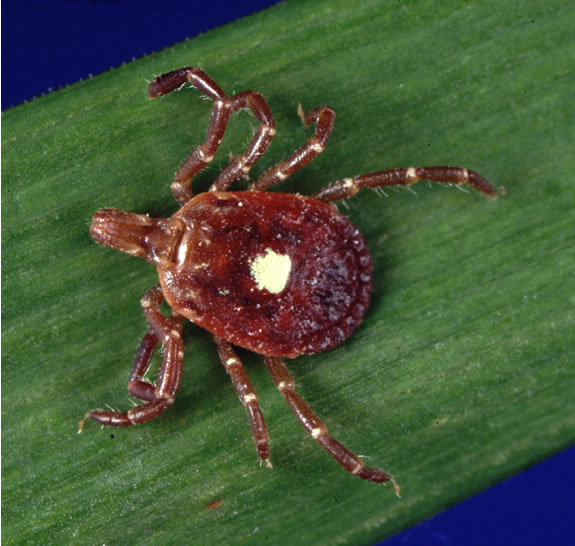

Once rare in Southeastern PA, Lone Star ticks are increasingly common. Females sport a single white dot on their back, and males have faint patterns along their edges.
They thrive in brushy woods and along wildlife corridors, and they’re aggressive biters.
These ticks can transmit ehrlichiosis and have been associated with alpha-gal syndrome, a red meat allergy linked to their bites.
Levittown, Pennsylvania, is a historic and family-friendly community located in Bucks County, known for its classic suburban charm and well-planned neighborhoods. With an abundance of parks like Falls Township Community Park, the Levittown Lake, and the scenic Silver Lake Nature Center nearby, residents enjoy plenty of opportunities for outdoor activities. However, Levittown’s humid summers, ample green space, and nearby water features contribute to an ideal environment for mosquito and tick populations to thrive.
Residents of Levittown are exposed to seasonal risks associated with mosquito-borne illnesses such as West Nile Virus and Zika Virus, in addition to tick-borne diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. With backyard barbecues, community events, and outdoor play being an essential part of local life, it’s crucial to take a proactive approach to mosquito and tick management to maintain both comfort and public health.
To help reduce exposure and activity around your property:
Remove standing water from areas such as birdbaths, plant pots, and clogged gutters.
Apply EPA-registered insect repellent and wear long sleeves and pants, especially at dawn and dusk.
Schedule consistent mosquito and tick treatments for your yard and common areas.
The Bucks County Department of Health maintains mosquito control programs throughout the region, including truck-mounted treatment efforts when necessary to manage local mosquito populations and limit disease transmission.

Levittown experiences warm, humid summers and chilly winters, creating a long mosquito and tick season from mid-spring through early fall. Moisture from rainfall and irrigation, coupled with the area’s dense vegetation and proximity to creeks and wetlands, supports mosquito breeding and creates harborage for ticks.
Key Factors Influencing Pest Activity:
Mosquitoes and Neighborhood Water Sources: Levittown’s access to lakes, ponds, and stormwater drains means mosquito populations can build up quickly during peak summer months.
Ticks and Suburban Landscaping: Wooded perimeters, untrimmed shrubs, and shady lawns offer ticks the cool, moist environments they prefer, particularly during the late spring and early fall seasons.
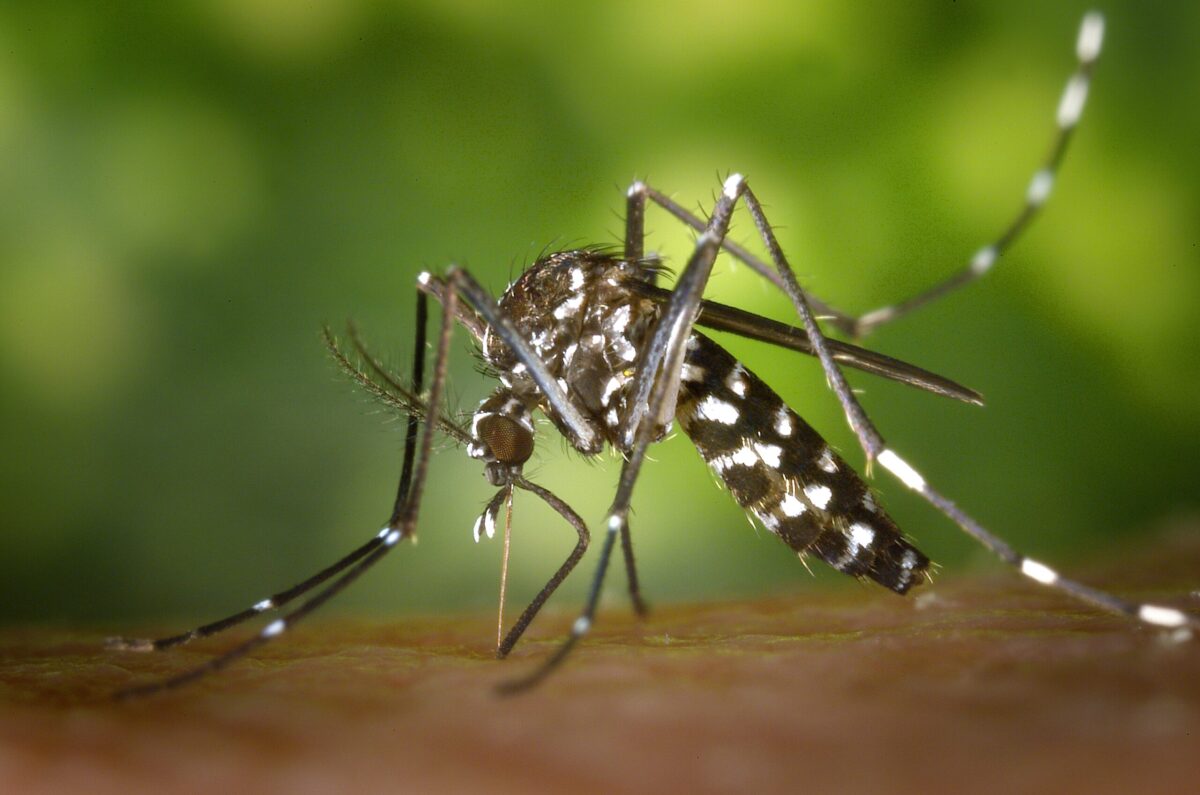


Identification: Black with a distinctive white stripe down the back and banded legs.
Habitat: Found around patios, wooded edges, and yards with dense vegetation or standing water in items like toys and birdbaths.
Behavior: Daytime biter, often targets ankles and lower legs.
Health Risks: Can transmit Zika, West Nile, and dengue viruses.
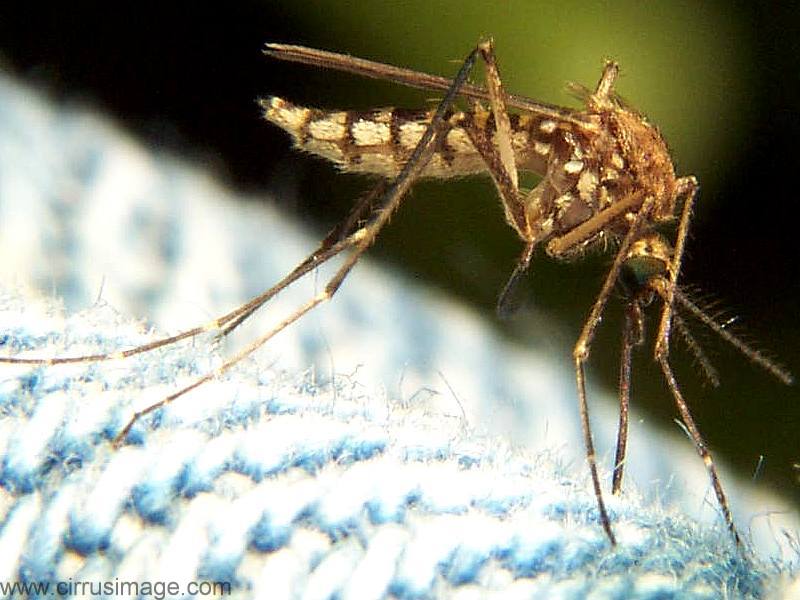

Identification: Brown body with white banding on the legs and abdomen.
Habitat: Common in floodplain fields, roadside ditches, and any area that holds temporary water after rain.
Behavior: Most active around dusk and after heavy rains.
Health Risks: Can cause severe biting irritation and may play a role in spreading West Nile virus.
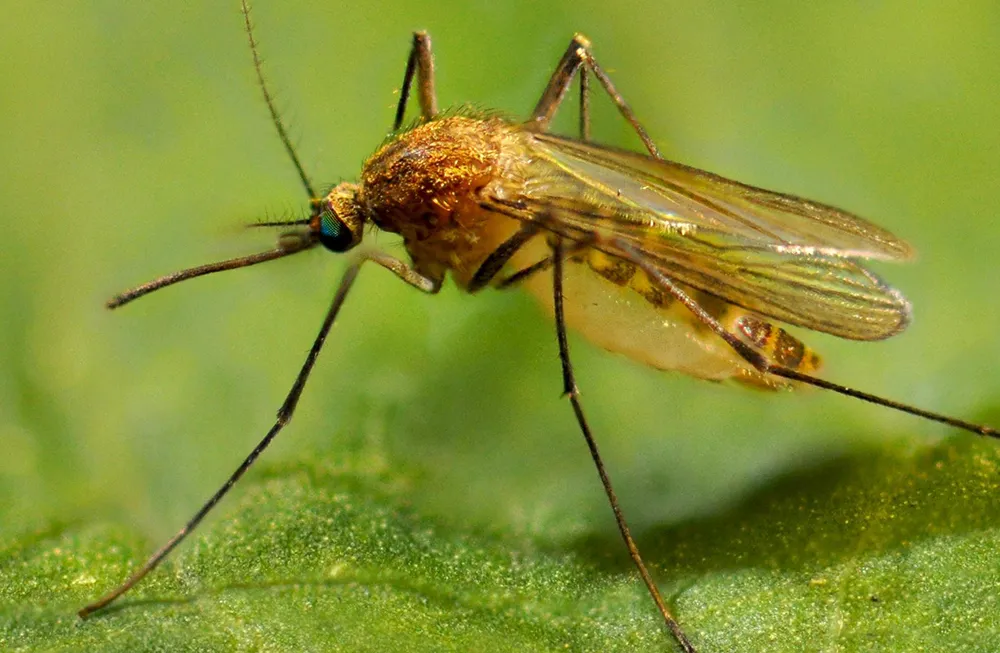

Identification: Light brown with darker bands across the abdomen.
Habitat: Breeds in stagnant water sources such as clogged gutters, rain barrels, and catch basins.
Behavior: Nocturnal biter that prefers birds but will feed on humans.
Health Risks: Primary vector for West Nile virus in Pennsylvania.

Identification: Medium-sized with four dark wing spots and an angled resting posture.
Habitat: Clean, slow-moving water like ponds, marshes, and creek edges.
Behavior: Active during dusk and dawn, especially in rural and semi-wooded areas.
Health Risks: Historically a malaria vector; currently causes irritating bites.

Key Activity: Mosquito activity begins as temperatures rise and spring rainstorms hit.
Breeding: Flooded lawns, puddles, and debris-filled containers become early-season breeding sites.
Common Species Active: Aedes vexans and Culex pipiens begin to emerge.
Behavior: Evening and early morning bites become more frequent by late spring.

Key Activity: Peak mosquito season—heat and humidity drive aggressive breeding.
Breeding: Anywhere water stands: gutters, planters, kiddie pools, and drainage ditches.
Common Species Active: Aedes albopictus, Aedes vexans, and Culex pipiens dominate.
Behavior: Biting pressure is high all day long, especially in shaded or wooded areas.

Key Activity: Activity decreases but persists through mild fall weather.
Breeding: Rainfall and leaf-clogged drains continue to provide habitat.
Common Species Active: Culex pipiens and some Aedes species remain present.
Behavior: Bites are common on warm fall days, especially during leaf removal and yard work.

Key Activity: Most mosquito activity halts due to colder temperatures.
Eggs: Aedes eggs remain dormant in dry locations, hatching once spring returns.
Adults: Culex mosquitoes may overwinter in basements, crawlspaces, and sheds.
Behavior: Warm winter spikes can trigger brief mosquito activity, especially after rain.
